|
|
|
Temperate forests
are typical of all European continent,
the Eastern region of Asia (in special,
Chinese and Japan) and North America.
Also are finded in tempered areas
of South America. Great part of them
has been destroyed for the wood obtaining
and the advantage of the ground with
farming aims.
The vegetation is
predominantly arboreal, although also
there are shrubs and herbaceous plants.
Within this biome are distinguished
two formation: the forest caducifolio
and the one of coniferous. The average
temperature in temperate forests is
50° F. Summers are mild, and average
about 70° F, while winter temperatures
are often well blow freezing. The
average yearly precipitation is 30-60
inches.
This precipitation
falls throughout the year, but in
the winter it falls as snow. The aggravating
factor is the water, because a period
of the year exists in which the precipitations
are smaller. To be remote of the tropical
zone is subject to the change of the
stations.
The development
of shrub and herbaceous vegetation
in this biome facilitated by the falling
leaf in winter, that allows that the
solar rays reach the ground during
the rest of the year. The sedimentation
of dead leaves contributes to mineral
salts and organic matter, that fertilize
the ground.
Another important
characteristic of the temperate forest
is the diversity of animal species:
birds, rodents, red deers, wild boars
and bears, among others, in the North
hemisphere, and in general, smaller
species that occupy equivalent ecological
niches in the south. The herbivorous
consume grass, fruits and berries,
and serve as food to the pregivers.
The man finds in
this biome an important source of
income. Of the reserves of the forest
raw materials for the industries;
nutritional, lumber, wastebasket and
pharmaceutics are extracted. The forests
also serve like containment means
and regulation of the water volumes,
conserves the quality of grounds and
it protect them of the erosion. In
another aspect, they contribute to
maintain the heat balance of the Earth
when absorbing present carbon dioxide
in the atmosphere.
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
In the temperate
forest coexist, among other
species, birds, rodents, foxes,
red deers and bears, consequently,
the cutting of trees, not only
it affects vegetal species sometimes
but animals, also causing extinction
risks.
|
|
|
|
 |
The
ground of the temperate forest
has a high content of organic
matter that is fundamentally accumulated
in the first two undercoat, which
is demonstrated by the dark colour
of the same ones. |
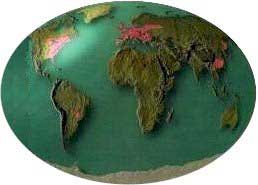
GEOGRAPHIC
DISTRIBUTION OF THE FORESTS
|
|
The caducifolio
forest
In the North
hemisphere, the caducifolio
forest is located around the
50 ' of North latitude.
It is characterized
by a mixed vegetal formation
and by the abundance of trees
that fall during the cold season.
The main arboreal species are
the oaks, the brown, the linden
trees, the maples, the elm trees,
the hazels and the cherry trees.
In the caducifolio
forest lives red wild boars,
squirrels and red deers, that
are herbivorous, and savage
foxes, bears and other carnivorous
mammals. Between the birds are
cuckoos, red headed and doves
that feeds on seeds and insects,
and others of plundering, like
the sparrow hawks, that look
for small birds.
|
|
|
An example
of this biome is the forests
Andean-patagonik that occupy
an extension of 63,000 km2 between
Argentine and Chile. The principal
trees are the lenga, the ñire,
the araucaria, the coihue, the
larch and the arrayán;
in the chilean slope, very humid,
lichens and fungi also abound.
Between the animals they are
the red fox, the pudú,
huemul or patagonik red deer,
the cóndor, and others,
some of them in extinction danger.
|
|
| |
|
The coniferous
forest
The coniferous
forest extends between the limit
of the tundra and the 50 ' of
N latitude, in Europe, Asia
and North America.
|
|
It is developed with precipitations
of about 500 annual mm. The
flora and the fauna are similar
to both sides of the Atlantic.
150 varieties of pines exist,
that grow in poor grounds.
The firs,
however, are preferably in rich
and humid lands. Other arboreal
species are the larches and
the cypresses; the birches grow
more in cold areas, near the
tundra.
The ground
is always covered by leaves
and branches fallen that offer
feeding to the herbivorous,
like the reindeer.
Between the
carnivorous are the marta,
|
|
|
that hunts on the branches of
the trees, and the lynx, a feline
that generally lives in the mountainous
areas. |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|

 cargando el contenido
cargando el contenido