|
More of 14% of the
surface of the planet it is occupied
by deserts, located mainly in neighboring
areas to the tropical. In this biome
the aggravating factor is the water:
the precipitations do not arrive at
15 inches per year, whereas the annual
average temperature is of 86 F. The
deserts are not dead regions. After
a sudden rain, a sandy surface can
be populated with plants, flowers
and small animals.
The dominant vegetation
is herbaceous and of character xerófilo,
that is to say, adapted to the dryness
of the environment. The distance of
the sea causes that the marine winds
arrive without humidity in the cold
continental deserts, like the one
of Gobi, in Mongolia.
|
Also
contribute to dryness
the sea cold currents
that happen through the
coasts of some continents
forming strips desert,
like the one of Atacama,
in Chile. In the warm
tropical deserts, like
the Sahara, the water
steam shortage in the
atmosphere does that a
90% of the heat of the
sun arrive to the ground.
|
|
| At
night, the temperature quickly
drops because the heat dissipates
in the atmosphere. |
|
|
The
Sahara
The
most extensive desert
of the world is the Sahara.
|
|
|
It extends on almost
9.000.000 of km2, in North Africa
and the Arabic peninsula. It registers
the maximum temperatures of the planet
(until 136 F), and has three types
of land: rocky plateaus, deserts of
stones, extensions where the sand
forms dunes of up to 200 ms of height.
In ancient times the Sahara had water
in sufficient amount, with very rich
flora and fauna, according to testifies
paintings on rocks of about 5,000
years ago.
 |
 |
The grounds
of the deserts are, in general,
extremely barren and are compound
of sand. In spite of the hardness
conditions, where the water arises
appear the oases, very rich in
vegetation. |
|
|
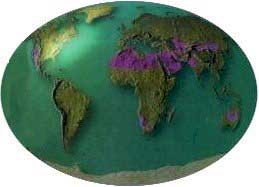
GEOGRAPHIC
DISTRIBUTION OF THE DESERTS
|
|
|
Rain, source
of life
In general,
rains do not keep a seasonal
rate.
Some deserts
have more precipitations in
winter; in others, can not rain
during ten years. The seeds
survive protected by their hard
crusts; when it rains, always
torrentially, germinate quickly.
Quickly the plants grow, bloom
and generate new seeds. Those
that does not die immediately,
must resist the dry climate
and, by a mechanism of adaptation
to the drought, absorb and conserve
water.
|
The American cactus,
for example, stores it in its stem;
the leaves, transformed into thorns,
do not eliminate water and defend
the plant. The photosynthesis process
takes place in the superficial cells
of the trunk. In general, the plants
of the desert have very deep roots
to catch the underground humidity,
and grow very remote of others to
take advantage of the water.
With the vegetal
life the fauna also renews. It appears
numerous insects, spiders, scorpions
and centipede. In the ponds that temporally
form, activate eggs of crustaceans
that have been long time - sometimes,
decades in latency. Frogs and toads
are multiplied, but when water evaporates
they buried to escape from the heat.
In the reptiles of the desert, the
grudges avoid the loss of water. The
mammals that prevail are rodent excavators,
who feed themselves on seeds. They
have strong later legs, with which
they jump and move quickly. The kangaroo
rat lives in the American deserts;
jerbo and the rate of the desert,
in Africa, and the marsupial kangaroo
in Australia. Only in the neighbourhoods
of the ponds some species of herbivorous
can subsist. Certain African zebras
detect the underground water presence,
and construct their water through
excavating with the hooves.
The camel, typical
of the deserts of Africa and Asia,
can pass lengths periods without drinking.
In case of necessity they undergo
the transformation of the greasy cells
of the hump, that provide water to
the organism. Those fat reserves can
surpass the 100 kilograms, and to
be concentrated in the hump they do
not transmit heat to the body.
The oasis
In the deserts of
Asia and Africa it is called oasis
to small islands of vegetation and
fauna concentration. Its location
throughout the territory determined,
in prehistoric times, the human migrations
and the routes of the caravans. In
its margins villages and cities arose.
An oasis is a potable water permanent
font, a spring next to which grows
palms, olive trees and fruit trees,
and agricultural activities and of
livestock farming can be developed.
In several African and Asian countries
it has been tried, successfully, to
create artificial oasis by means of
the extraction of the deep water.
 |
|
|
| In spite
of the extreme dryness and the
heat, the deserts are not dead
regions. To the dusk or when the
night falls, birds, reptiles,
rodents begin to show. |
|
|
|

 cargando el contenido
cargando el contenido